MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
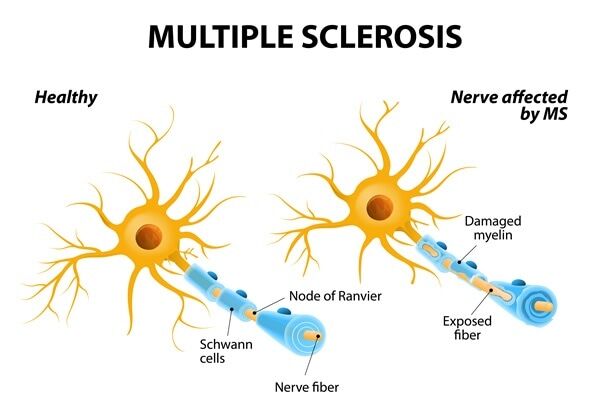
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a disease of the central nervous system in which your immune system attacks the coating, called myelin, of the nerve cells. MS predominantly affects young adults during their most productive years. Genetic and environmental factors are known to contribute to Multiple Sclerosis, but a specific cause for this disease is unknown.
Disease begins most commonly with acute display of neurologic abnormalities. Symptoms vary dramatically from person to person and over the course of the disease depending on the location of affected nerve fibers.
For more information on Multiple Sclerosis, visit the National Multiple Sclerosis Society at www.nationalmssociety.org.
Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis:
Multiple sclerosis symptoms differ greatly and often affect movement:
- Numbness or muscle weakness in one or more limbs that typically occurs on one side of your body at a time, or the hands, legs and trunk
- Tingling and burning sensations, numbness, and chronic pain with certain neck movements, especially bending the neck forward
- Tremor, lack of coordination or unsteady balance
- Problems with sexual, bowel and bladder function
- Slurred speech
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
Vision problems are also common, including:
- Partial or complete loss of vision, usually in one eye at a time, often with pain during eye movement
- Prolonged double vision
- Blurry vision
Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis:
There are no specific tests for MS. Instead, a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis often relies on ruling out other conditions that might produce similar signs and symptoms. The assessment includes neurological findings, clinical observation, results of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (presence of areas of demyelination in the CNS), spinal fluid examination (presence of oligoclonal bands and/or elevated IgG index). Your doctor may include an evoked potential test which uses a visual stimuli or electrical stimuli, in which you watch a moving visual pattern, or short electrical impulses are applied to nerves in your legs or arms.
Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis:
There is no cure for multiple sclerosis. Treatment typically focuses on speeding recovery from attacks, slowing the progression of the disease and managing MS symptoms. Some people have such mild symptoms that no treatment is necessary. However, a number of medications can be used to treat the disease symptoms, including but not limited to:
Corticosteroids
Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis)
Your doctor may order a more advanced therapy of biologic injections or infusions. AZIV Infusion provides the following biologic injections and infusions in a convenient and comfortable setting for patients seeking treatment for Multiple Sclerosis: