NEUROPATHY
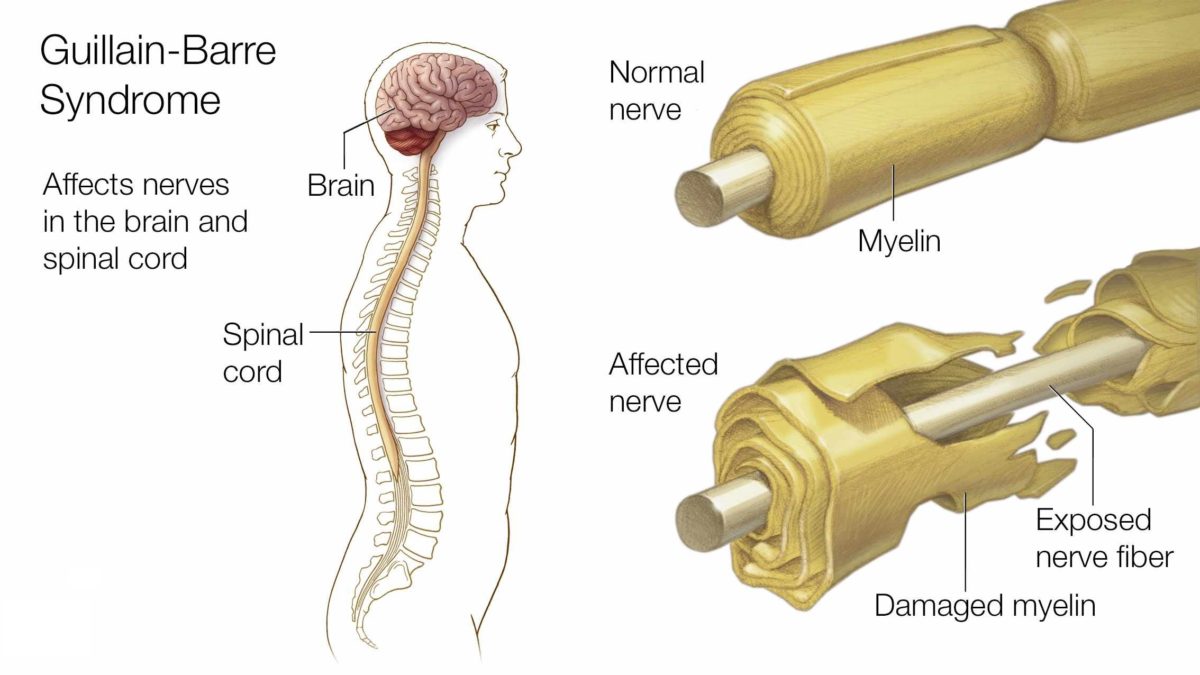
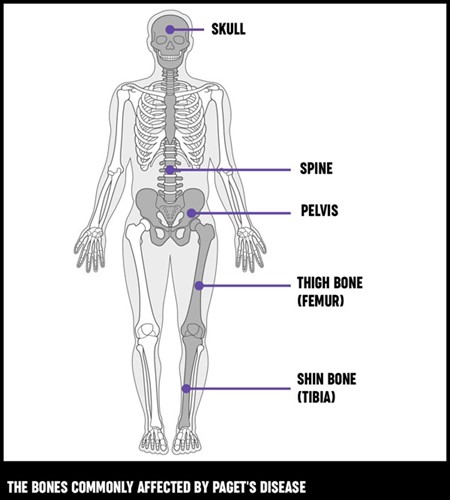
Peripheral neuropathy (new-ROP-uh-thee) is damage or disease to your peripheral nerves — the nerves that carry information to and from your brain and spinal cord and the rest of your body, such as your arms and legs. The peripheral nerves make up an intricate network that connects the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, skin, and internal organs.
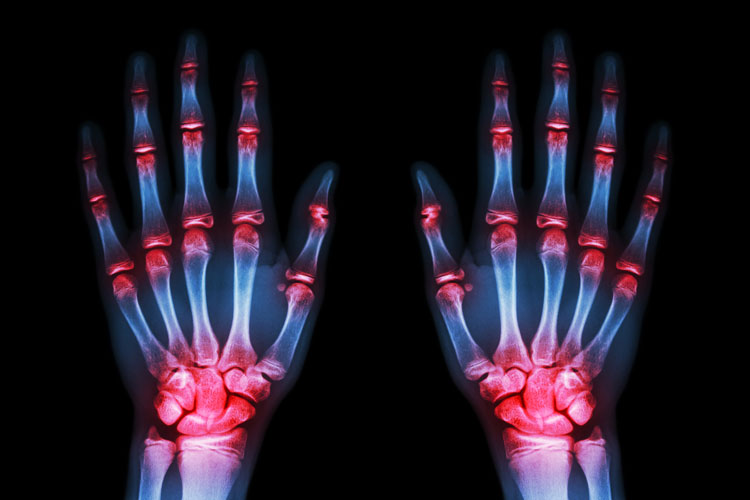
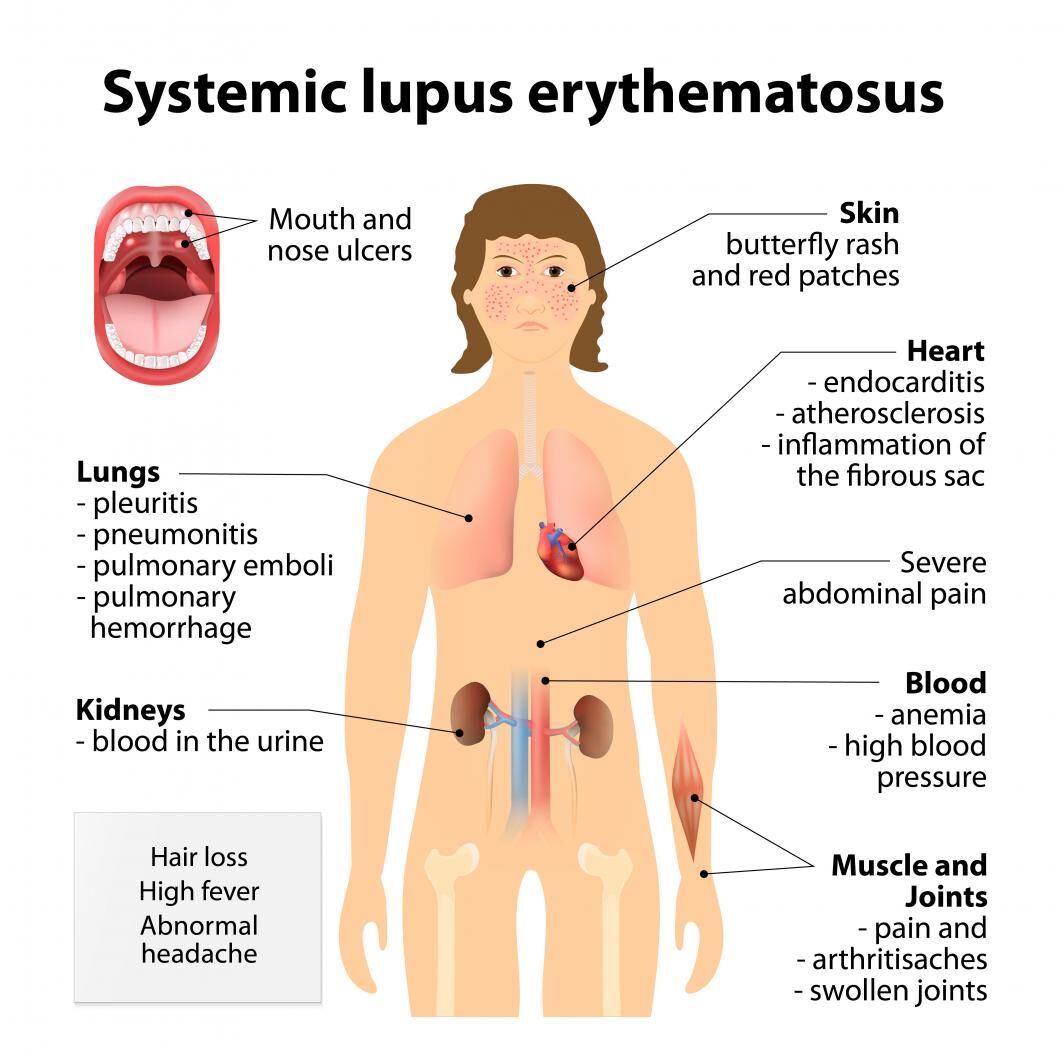
Peripheral neuropathy can result from traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic problems, inherited causes and exposure to toxins. One of the most common causes is diabetes.
To learn more about Neuropathy and other related diseases visit the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) website. The site provides a wide variety of educational information for patients, caregivers, clinicians and researchers to specific rare diseases. Information may also be located at the American Diabetes Association.
Symptoms of Neuropathy:
Peripheral neuropathy can result from traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic problems, inherited causes and exposure to toxins. One of the most common causes is diabetes. Those with neuropathy often describe the pain as stabbing, burning or tingling. In many cases, symptoms improve, especially if caused by a treatable condition.
Every nerve in the peripheral system has a specific function; therefore, symptoms depend on the type of nerves affected. Nerves are classified as follows:
- Sensory nerves that receive sensation, such as temperature, pain, vibration or touch, from the skin
- Motor nerves that control muscle movement
- Autonomic nerves that control functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, digestion and bladder
Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include:
- Gradual onset of numbness, prickling or tingling in your feet or hands, which can spread upward into your legs and arms
- Sharp, jabbing, throbbing or burning pain
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Pain during activities that shouldn’t cause pain, such as pain in your feet when putting weight on them or when they’re under a blanket
- Lack of coordination and falling
- Muscle weakness
- Feeling as if you’re wearing gloves or socks when you’re not
If autonomic nerves are affected, symptoms might include:
- Heat intolerance
- Excessive sweating or not being able to sweat
- Bowel, bladder or digestive problems
- Changes in blood pressure, causing dizziness or lightheadedness
Diagnosis of Neuropathy:
Peripheral neuropathy has many potential causes, so doctors are sometimes unable to pinpoint the exact cause of an acquired neuropathy. The diagnosis of neuropathy may include a physical exam, blood tests, imaging tests, nerve function test and a nerve and/or skin biopsy.
Treatment of Neuropathy:
The treatment goal of neuropathy is to manage the condition causing your neuropathy and to relieve symptoms.
Medications can reduce the pain of peripheral neuropathy.
- Pain relievers
- Anti-seizure medications
- Topical treatments
- Antidepressant
AZIV Infusion provides the following biologic injections and infusions in a convenient and comfortable setting for patients seeking treatment for Neuropathy: